✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
RNeasy Plus Universal Mini Kit (50)
Cat no. / ID. 73404
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- High yields of total RNA from all tissues
- Fast non-enzymatic removal of genomic DNA
- Streamlined QIAzol lysis and RNeasy 96 purification
- Pure, high-quality RNA without phenol contamination
- High-performance RNA for all downstream applications
Product Details
The RNeasy Plus Universal Mini Kit integrates fast, convenient RNA purification with effective elimination of genomic DNA. Optimized protocols enable purification of high-quality RNA from any type of tissue, even difficult-to-lyse tissues. The kit includes QIAzol Lysis Reagent for lysing fatty tissue and other types of tissue and RNeasy spin columns for purifying high-quality RNA. The RNeasy Plus Universal Mini Kit can be automated on the QIAcube Connect.
The RNeasy 96 Universal Tissue Kit enables total RNA purification in 96-well format from any tissue. Tissues are efficiently lysed and homogenized in QIAzol Lysis Reagent, and high-quality RNA is purified using silica-membrane RNeasy 96 plates. Manual purification is carried out using the QIAGEN Centrifuge 4-16KS and, optionally, the QIAvac 96 vacuum manifold. Automated purification using the related RNeasy 96 Universal Tissue 8000 Kit is performed on the BioRobot Universal System. Tissue samples can be conveniently stabilized using Allprotect Tissue Reagent, and efficiently disrupted using the TissueLyser II. Nonfatty tissues can be stabilized using the RNAprotect Tissue Reagent.
Performance
The RNeasy Plus Universal procedure allows high, reproducible RNA yields from any type of tissue, including fatty tissues and difficult-to-lyse tissue (see table “Typical yields of total RNA using the RNeasy Plus Universal Mini Kit”). Yields can vary due to factors such as species and developmental stage, especially with adipose tissues.
| Mouse/rat tissue (10 mg) | Yield of total RNA ((µg) |
|---|---|
| Adipose tissue | 0.5–2.5 |
| Brain | 5–20 |
| Heart | 5–25 |
| Intestine | 10–60 |
| Kidney | 5–40 |
| Liver | 15–80 |
| Lung | 5–15 |
| Muscle | 5–35 |
| Skin | 2–5 |
| Spleen | 15–100 |
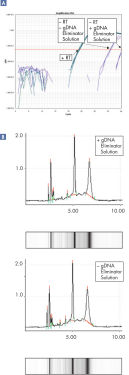
Analysis of purified RNA by real-time RT-PCR, and on the QIAxcel system, demonstrates high-quality RNA with good integrity (see figure " High-quality RNA"). gDNA Eliminator Solution and RNeasy technologies efficiently remove most of the genomic DNA contamination without DNase treatment (see figure " Effective removal of genomic DNA").
Compared with standard silica-membrane procedures, the RNeasy 96 system provides higher yields of total RNA for all tissue types (see table “Typical total RNA yields using the RNeasy 96 Universal Tissue Kit”).
Typical total RNA yields using the RNeasy 96 Universal Tissue Kit
| Tissue | RNA yield* (µg per 10 mg of tissue) |
|---|---|
| Kidney | 5–40 |
| Liver | 15–80 |
| Lung | 5–15 |
| Heart | 5–25 |
| Muscle | 5–35 |
| Brain | 5–20 |
| Adipose tissue | 0.5–2.5 |
| Spleen | 15–100 |
| Intestine | 10–60 |
| Skin | 2–5 |
High-quality RNA can be isolated from tissues preserved either by freezing or by stabilization with RNAprotect at room temperature (see figure "High-quality total RNA from rat liver and muscle tissue"). Intact RNA purified from difficult-to-lyse fibrous and fatty tissues is suitable for downstream applications (see figures " High-quality RNA from skin / adipose / liver / intestine tissue" and " Real-time analysis of high-quality RNA from rat brain").
See figures
 Effective removal of genomic DNA.
Effective removal of genomic DNA.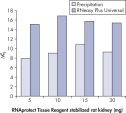 High quality total RNA from rat liver and muscle tissue.
High quality total RNA from rat liver and muscle tissue.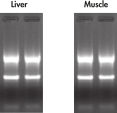 High-quality RNA from skin tissue.
High-quality RNA from skin tissue.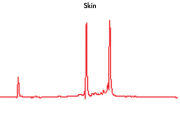 High-quality RNA from adipose tissue.
High-quality RNA from adipose tissue.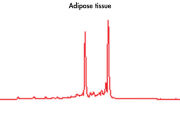 High-quality RNA from liver tissue.
High-quality RNA from liver tissue.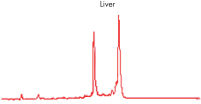 High-quality RNA from intestine tissue.
High-quality RNA from intestine tissue.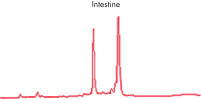 Real-time analysis of high-quality RNA from rat brain.
Real-time analysis of high-quality RNA from rat brain.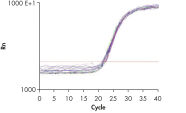
Principle
The RNeasy Plus Universal Mini procedure enables purification of RNA from any type of tissue, including fatty or difficult-to-lyse tissues. The RNeasy Plus Universal Mini Kit integrates phenol/guanidine-based sample lysis and silica-membrane purification of total RNA. QIAzol Lysis Reagent, included in the kits, is a monophasic solution of phenol and guanidine thiocyanate, designed to facilitate lysis of all kinds of tissues and to inhibit RNases. The highly efficient lysis and the subsequent removal of contaminants by organic phase extraction enable the use of larger amounts of tissue with RNeasy spin columns. gDNA Eliminator solution effectively removes genomic DNA contamination and significantly improves separation of DNA into the interphase.
The RNeasy 96 Universal Tissue procedure enables high-throughput purification of RNA from any animal or human tissue sample. Compared with standard silica-membrane procedures, the RNeasy 96 Universal Tissue Kit provides higher yields of total RNA for all tissue types. The RNeasy procedure enriches for RNA >200 bases long, providing a yield of total RNA that does not include 5.8S rRNA, tRNA, and other low-molecular weight RNAs, which make up 15–20% of total cellular RNA.
Procedure
The RNeasy Plus Universal procedure is easy to follow and, compared to using phenol/chloroform to extract total RNA with a subsequent cleanup procedure, much faster and more efficient with better RNA purity and yield (see flowchart " RNeasy Plus Universal Mini procedure"). Total RNA is purified from up to 50 mg tissue using the RNeasy Plus Universal Mini Kit.
Tissue samples are homogenized in QIAzol Lysis Reagent using the TissueRuptor II, TissueLyser LT, or TissueLyser II. After addition of gDNA Eliminator Solution and chloroform, the homogenate is separated into aqueous and organic phases by centrifugation. The upper, aqueous phase with RNA is collected, mixed with ethanol, and RNA is purified using RNeasy spin columns. Total RNA binds to the spin column membrane, and phenol and other contaminants are efficiently washed away. High-quality RNA is eluted in RNase-free water.
The procedure provides an enrichment for mRNA since most RNAs <200 nucleotides (such as rRNAs and tRNAs) are excluded. The RNeasy Plus Universal procedure can be modified to allow the purification of total RNA containing small RNAs, such as miRNA, from cultured cells.
The optimized RNeasy 96 Universal Tissue procedure integrates TissueLyser / QIAzol processing with RNeasy 96 purification in an easy-to-follow protocol (see flowchart " RNeasy 96 Universal Tissue procedure"). Efficient high-throughput disruption using the TissueLyser II provides parallel disruption and homogenization, with lysis of up to 192 samples in QIAzol Lysis Reagent. Protocol steps are performed manually using the QIAGEN 96-Well-Plate Centrifugation System, with optional use of the QIAvac 96 vacuum manifold.
See figures
Applications
RNA purified using RNeasy Plus Universal Kits is ideally suited for downstream applications that are sensitive to low amounts of DNA contamination, such as RNA-seq, quantitative real-time RT-PCR. The purified RNA can also be used in other applications.
The combination of QIAzol and RNeasy technologies results in highly pure RNA without phenol carryover. RNA purified using the RNeasy 96 Universal Tissue Kit is suitable for all downstream applications, including RNA-seq, real-time RT-PCR and array analysis.
| Features | RNeasy Plus Universal Mini Kit | RNeasy 96 Universal Tissue Kit |
|---|---|---|
| Applications |
Northern, dot, and slot blotting, end-point RT-PCR, quantitative, real-time RT-PCR, array analysis, next-generation sequencing |
PCR, qPCR, real-time PCR |
| Elution volume | 30 µl; | 45–70 µl |
| Format | Mini | 96-well plate |
| Integrated removal of genomic DNA | Yes | No |
| Main sample type | Tissue samples including difficult-to-lyse and demanding tissues | Tissue samples |
| Processing | Manual (centrifugation), automated (QIAcube Connect) | Manual (centrifugation or vacuum) |
|
Purification of total RNA, miRNA, poly A+ mRNA, DNA or protein |
RNA | RNA |
| Sample amount | 5–50 mg | 25–100 mg |
| Technology | QIAzol/spin column technology | Silica technology |
| Yield | Varies | Varies |
Supporting data and figures
High-quality RNA.