✓ 연중무휴 하루 24시간 자동 온라인 주문 처리
✓ 풍부한 지식과 전문성을 갖춘 제품 및 기술 지원
✓ 신속하고 안정적인 (재)주문
MinElute Reaction Cleanup Kit (50)
카탈로그 번호 / ID. 28204
✓ 연중무휴 하루 24시간 자동 온라인 주문 처리
✓ 풍부한 지식과 전문성을 갖춘 제품 및 기술 지원
✓ 신속하고 안정적인 (재)주문
특징
- 매우 적은 용출량
- 신속한 절차 및 간편한 취급 방법
- 재현성이 뛰어난 높은 회수율
- 편리한 샘플 분석을 위한 겔 로딩 염료
제품 세부 정보
MinElute Reaction Cleanup Kit는 효소 반응에서 70bp~4kb 크기의 DNA의 실리카 막 기반 정제를 위한 스핀 컬럼, 완충액, collection 튜브를 제공합니다. 스핀 컬럼은 매우 적은 용량(최소 10µl)으로 용출할 수 있도록 설계되어 고농축 DNA를 높은 수율로 얻을 수 있습니다. 포함된 pH indicator 염료를 통해 스핀 컬럼에 결합하는 DNA에 대한 최적의 pH를 쉽게 파악할 수 있습니다. 해당 절차는 QIAcube Connect에서 완전히 자동화할 수 있습니다. MinElute system으로 정제된 DNA 절편은 염기서열 분석, 마이크로어레이 분석, 결찰(ligation) 및 형질전환, 제한효소 처리(restriction digestion), 라벨링, 미세 주입, PCR 및 체외 전사를 포함한 모든 응용 분야에서 바로 사용할 수 있습니다.
최적의 결과를 얻으려면 이 제품을 QIAvac 24 Plus와 함께 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
성능
MinElute Reaction Cleanup Kit는 효소 반응에서 최대 5µg의 DNA(70bp~4kb)를 클린업하여 다양한 응용 분야에 적합한 높은 수율의 DNA를 제공합니다. 이 키트는 효소 반응 클린업을 위한 스핀 컬럼을 제공합니다. 마이크로 원심분리기 또는 진공 매니폴드를 사용하여 고농도의 DNA 절편(70bp~4kb)을 빠르게 얻을 수 있습니다. (4kb보다 큰 DNA 절편은 QIAquick System을 사용하여 정제해야 합니다.)
| 단백질 | 효소 소단위당 분자량(kDa) |
|---|---|
| DNA 중합효소 I | 109 |
| Klenow fragment | 62 |
| 송아지 장 알칼리성 인산분해효소 | 69 |
| T4 DNA ligase | 55 |
| T4 Polynucleotide kinase | 35 |
| 말단 전달효소 | 32 |
| DNase I | 31 |
| 제한 효소 | 다양함 |
원리
MinElute Kit에는 염도가 높은 완충액에서 DNA를 결합하고 저염 완충액 또는 물로 용출하기 위한 실리카 막 어셈블리가 포함되어 있습니다. 정제 절차에서 DNA 샘플에서 프라이머, 뉴클레오타이드, 효소, 미네랄 오일, 염, 아가로스, 브로민화 에티듐(ethidium bromide) 및 기타 불순물을 제거합니다. 실리카 막 기술은 분산 수지 및 슬러리(slurry)와 관련된 문제와 불편을 해소합니다. 특수 결합 완충액은 각 응용 분야에 최적화되어 있으며 특정 크기 범위 내에서 DNA 분자를 선택적으로 흡착하도록 합니다.
겔 로딩 염료
더 빠르고 편리한 샘플 처리 및 분석을 위해 겔 로딩 염료가 제공됩니다. GelPilot 로딩 염료는 아가로스 겔 실행 시간을 최적화하고 작은 DNA 절편이 너무 멀리 이동하는 것을 방지하기 위해 세 가지 추적 염료(크실렌 시아놀, 브로모페놀 블루, 오렌지 G)를 함유하고 있습니다(그림 " GelPilot 로딩 염료" 참조).
그림 참조
절차
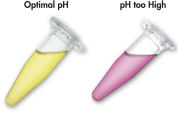
MinElute system은 간단한 결합-세척-용출 절차를 사용합니다(순서도 " MinElute 절차" 참조). 결합 완충액을 효소 반응물에 직접 첨가하고 혼합물을 MinElute 스핀 컬럼에 적용합니다. 결합 완충액에는 pH indicator 염료가 포함되어 있어 DNA 결합을 위한 최적의 pH를 쉽게 확인할 수 있습니다(그림 "pH indicator 염료" 참조). 핵산은 완충액의 높은 염도 조건에서 실리카 막에 흡착됩니다. 불순물을 씻어내고 제공된 소량의 저염 완충액 또는 물로 순수한 DNA를 용출하여 후속 응용 분야에 바로 사용할 수 있습니다.
취급
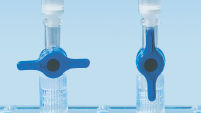
MinElute 스핀 컬럼은 두 가지 편리한 취급 옵션을 제공하도록 고안되었습니다(순서도 "MinElute 절차" 참조). 스핀 컬럼은 기존의 탁상용 마이크로 원심분리기 또는 루어 커넥터가 있는 모든 진공 매니폴드(예: QIAvac 24 Plus 또는 QIAvac Luer Adapters가 있는 QIAvac 6S)에 장착할 수 있습니다. MinElute Reaction Cleanup Kit는 다른 QIAGEN 스핀 컬럼 기반 키트와 더불어 QIAcube Connect에서 완전히 자동화할 수 있어 생산성을 높이고 결과를 표준화할 수 있습니다(그림 "스핀 컬럼 취급 옵션 A, B, C, D, E" 및 " QIAcube Connect" 참조).
그림 참조
응용 분야
MinElute System으로 정제된 DNA 절편은 다음을 포함한 모든 응용 분야에서 바로 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 염기서열 분석
- 마이크로어레이 분석
- 결찰(ligation) 및 형질전환
- 제한효소 처리(Restriction digestion)
- 라벨링
지원되는 데이터 및 수치
스핀 컬럼 취급 옵션 — E.

사양
| 특징 | 사양 |
|---|---|
| bindingcapacity | 5µg |
| fragmentsize | 70bp~4kb |
| elutionvolume | 10µl |
| recoveryoligonucleotidesdsdna | 회수: 올리고뉴클레오타이드, dsDNA |
| removal10mers1740mersdyeterminatorproteins | <40mers 제거 |
| format | 튜브 |
| sampletypeapplications | DNA, 올리고뉴클레오타이드: 효소 반응 |
| technology | 실리카 기술 |