QIAGEN Plasmid Kits zur Extraktion von Plasmid-DNA
Zur Aufreinigung von bis zu 10 mg Plasmid- oder Cosmid-DNA in Transfektionsqualität
Zur Aufreinigung von bis zu 10 mg Plasmid- oder Cosmid-DNA in Transfektionsqualität
✓ Automatische Verarbeitung von Online-Bestellungen 24/7
✓ Sachkundiger und professioneller technischer und Produkt-Support
✓ Schnelle und zuverlässige (Nach-)Bestellung
Kat.-Nr. / ID. 12125
✓ Automatische Verarbeitung von Online-Bestellungen 24/7
✓ Sachkundiger und professioneller technischer und Produkt-Support
✓ Schnelle und zuverlässige (Nach-)Bestellung
QIAGEN Plasmid Kits bieten Anionenaustauscherspitzen nach dem Schwerkraftprinzip für die Aufreinigung von Plasmid-DNA in Transfektionsqualität. Die Reinigung des Lysats und die Ausfällung mit Isopropanol erfolgt durch Zentrifugation.
Das QIAGEN Plasmid Mega Kit (Kat.-Nr. 12181) und das QIAGEN Plasmid Giga Kit (Kat.-Nr. 12191) können mit den QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridges (Kat.-Nr. 19781) als optionaler Protokollschritt zur schnellen Bereinigung bakterieller Lysate durch Filtration anstelle von Zentrifugation eingesetzt werden. Weitere Einzelheiten zum Grundprinzip siehe unten.
Die QIAGEN Plasmid Kits nutzen QIAGEN Anionenaustauscherspitzen nach dem Schwerkraftprinzip für eine effiziente Aufreinigung der Plasmid-DNA. Bis zu
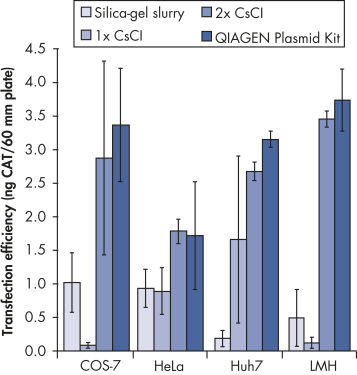
10 mg (Giga), 2,5 mg (Mega), 500 µg (Maxi), 100 µg (Midi) und 20 µg (Mini) Plasmid-DNA mit hoher Kopienzahl werden aus der Kultur aufgereinigt (das Kulturvolumen hängt von der Plasmid-Kopienzahl, der Größe des Inserts, dem Wirtsstamm und dem Kulturmedium ab). Mit QIAGEN Plasmid Kits aufgereinigte Plasmid-DNA eignet sich hervorragend für Anwendungen wie Transfektion (siehe Abbildung „ Transfektionseffizienz in Abhängigkeit vom Plasmid-Aufreinigungsverfahren“), Klonierung und In-vitro-Transkription.
Das innovative Anionenaustauscherharz in den QIAGEN-tips wurde ausschließlich für die Aufreinigung von Nukleinsäuren entwickelt. Seine hervorragenden Trenneigenschaften führen zu einer DNA-Reinheit, die der durch zwei aufeinanderfolgende Durchgänge der CsCl-Gradientenzentrifugation erzielten Reinheit gleichwertig oder überlegen ist. Vorgepackte QIAGEN-Spitzen arbeiten nach dem Schwerkraftprinzip und trocknen nie aus, so dass der Zeitaufwand für das manuelle Ansetzen von Plasmiden minimiert wird. Im gesamten QIAGEN Plasmid-Aufreinigungssystem kommen keine toxischen Substanzen wie Phenol, Chloroform, Ethidiumbromid und CsCl zum Einsatz, was die Gefahr für den Anwender und die Umwelt minimiert.
Als optionalen Protokollschritt zur schnellen Bereinigung von Bakterienlysaten durch Filtration anstelle der Zentrifugation können die QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridges (Kat.-Nr. 19781) verwendet werden, die mit hausinternem Vakuum arbeiten, um selbst große Mengen an Bakterienlysat mit minimalem Aufwand effizient zu bereinigen. Das Protokoll ist im Handbuch zu finden.
Merkmale |
Plasmid Mini Kit |
Plasmid Midi Kit |
Plasmid Maxi Kit |
Plasmid Mega Kit |
Plasmid Giga Kit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anwendungen | Transfektion, Klonierung, Sequenzierung, Kapillarsequenzierung usw. | Transfektion, Klonierung, Sequenzierung, Kapillarsequenzierung usw. | Transfektion, Klonierung, Sequenzierung, Kapillarsequenzierung usw. | Transfektion, Klonierung, Sequenzierung, Kapillarsequenzierung usw. | Transfektion, Klonierung, Sequenzierung, Kapillarsequenzierung usw. |
| Kulturvolumen/Ausgangsmaterial | 3–10 ml Kulturvolumen | 25–100 ml Kulturvolumen | 100–500 ml Kulturvolumen | 500 ml – 2,5 Liter Kulturvolumen | 2,5–5 Liter Kulturvolumen |
| Elutionsvolumen | Variabel | Variabel | Variabel | Variabel | Variabel |
| Plasmidtyp | High-Copy, Low-Copy, Cosmid-DNA | High-Copy, Low-Copy, Cosmid-DNA | High-Copy, Low-Copy, Cosmid-DNA | High-Copy, Low-Copy, Cosmid-DNA | High-Copy, Low-Copy, Cosmid-DNA |
| Verfahren | Manuell (Schwerkraftprinzip) | Manuell (Schwerkraftprinzip) | Manuell (Schwerkraftprinzip) | Manuell (Schwerkraftprinzip) | Manuell (Schwerkraftprinzip) |
| Probe pro Lauf | 1 Probe pro Lauf | 1 Probe pro Lauf | 1 Probe pro Lauf | 1 Probe pro Lauf | 1 Probe pro Lauf |
| Technologie | Anionenaustausch-Technologie | Anionenaustausch-Technologie | Anionenaustausch-Technologie | Anionenaustausch-Technologie | Anionenaustausch-Technologie |
| Dauer pro Lauf | 80 min | 150 min | 160 min | 220 min | 320 min |
| Ausbeute | <20 µg | bis zu 100 µg | <500 µg | <2,5 mg | <10 mg |
Bei den QIAGEN Plasmid Kits werden die Bakterienlysate durch Zentrifugation bereinigt. Das bereinigte Lysat wird dann auf die Anionenaustauscher-Spitze aufgebracht, wo die Plasmid-DNA unter geeigneten salzarmen und pH-Bedingungen selektiv bindet. RNA, Proteine, Metaboliten und andere niedermolekulare Verunreinigungen werden durch einen Waschschritt mit Waschlösung mit mittlerem Salzgehalt entfernt, und reine Plasmid-DNA wird in einem Puffer mit hohem Salzgehalt eluiert (siehe Flussdiagramm „ QIAGEN Plasmid Kit Verfahren“). Die DNA wird konzentriert, durch Isopropanol-Fällung entsalzt und durch Zentrifugation gesammelt.
Mit QIAGEN Plasmid Kits aufgereinigte Plasmid-DNA eignet sich hervorragend für Anwendungen wie z. B.:
| 12123 | 12125 | 12143 | 12145 | 12145X4 | 12162 | 12163 | 12165 | |
| Product | Plasmit Kit | Plasmit Kit | Plasmit Kit | Plasmit Kit | Plasmit Kit | Plasmit Kit | Plasmit Kit | Plasmit Kit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product Type | Kit | Kit | Kit | Kit | Kit | Kit | Kit | Kit |
| Column Type | Mini | Mini | MIDI | MIDI | MIDI | MAXI | MAXI | MAXI |
| Preparations | 25 | 100 | 25 | 100 | 400 | 10 | 25 | 100 |
| CatNo | Product | Product Type | Column Type | Preparations |
| 12123 | Plasmit Kit | Kit | Mini | 25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12125 | Plasmit Kit | Kit | Mini | 100 |
| 12143 | Plasmit Kit | Kit | MIDI | 25 |
| 12145 | Plasmit Kit | Kit | MIDI | 100 |
| 12145X4 | Plasmit Kit | Kit | MIDI | 400 |
| 12162 | Plasmit Kit | Kit | MAXI | 10 |
| 12163 | Plasmit Kit | Kit | MAXI | 25 |
| 12165 | Plasmit Kit | Kit | MAXI | 100 |
| Eigenschaften | Spezifikationen |
|---|---|
| technology | Anionenaustausch-Technologie |
| culturevolumestartingmaterial | 3ml–5 Liter Kulturvolumen |
| yield | <20 µg bis <10 mg |
| processing | Manuell (Schwerkraftprinzip) |
| samplesperrunthroughput | 1 Probe pro Lauf |
| timeperrunorprepperrun | 80–320 min |
| applications | Transfektion, Klonierung, Sequenzierung, Kapillarsequenzierung usw. |
| plasmidtype | High-Copy, Low-Copy, Cosmid-DNA |